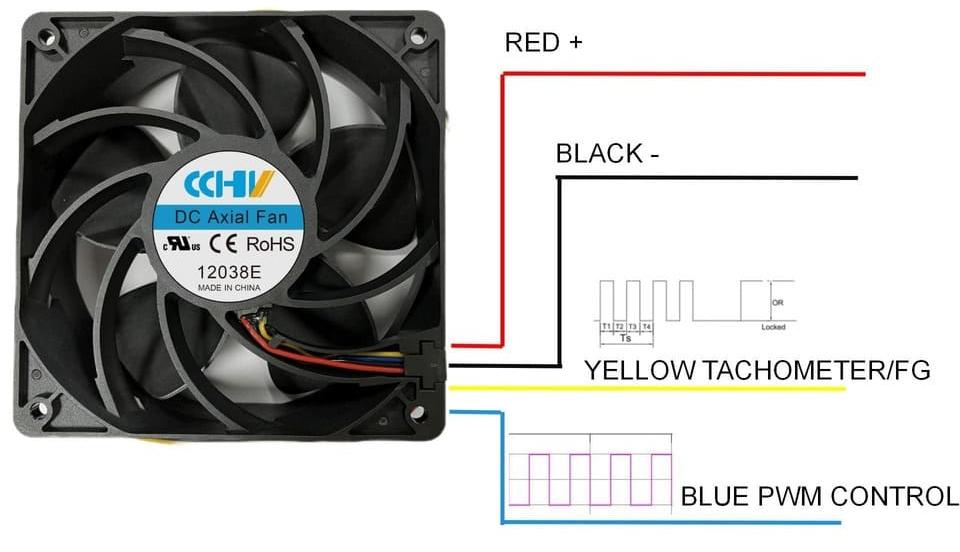
Just like how a hot summer day can be tough on us, equipment too can struggle with overheating, leading to a host of problems like breakdowns, shorter lifespans, and even safety hazards. This is where DC fans come into play, much like a cool breeze on a stifling day. Especially in hot environments, these fans are not just helpful; they’re a necessity for keeping things running smoothly. When it comes to DC fans, there are two main types – axial and centrifugal – different air delivery directions. Selecting the right one is crucial to ensure your equipment stays cool, efficient, and safe, avoiding the troubles that come with getting too hot.
In this article, we extensively explore in terms of definitions, working principles, and various applications. The knowledge we’ll share here is more than just technical; it’s about gaining a deeper understanding that empowers you. Whether you’re in the process of designing a brand-new system or upgrading an existing one, this information will not only enhance your technical skills but also provide you with valuable insights for making well-informed decisions. So, stay tuned as we delve into the complexities and subtle differences between these two types of DC fans. Together, we’ll explore this field with confidence and clarity.
Understanding Axial Fans
Axial Fans Designes and Working Principle
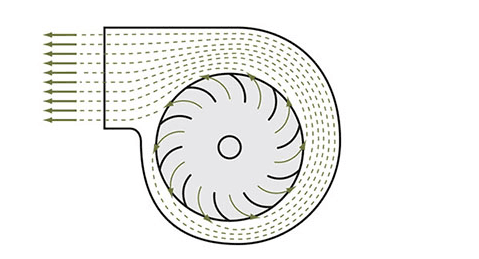
Axial fans are uniquely designed with their propellers (fan blades) situated in an annular airflow path between a cylindrical hub and the casing. This design effectively uses the curved shape of the blades to push air outward, generating airflow along the direction of the rotational axis. The airflow in axial fans moves parallel to this axis, contributing to their compact structure.
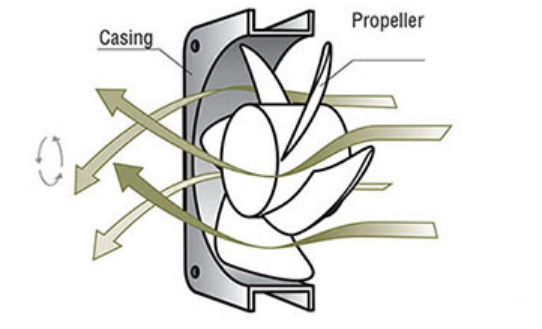
 Airflow forms in an annular path between a cylindrical hub and the casing. | 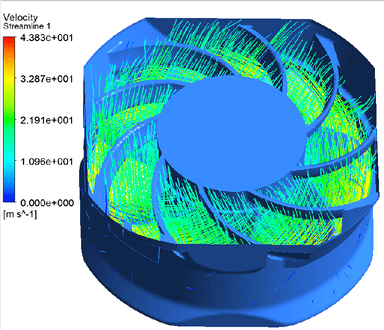 Airflow is forced to push out due to the the curved shape of the blades. |
Typical applications
Axial fan makes them highly efficient in producing a large volume of airflow, making them ideal for applications requiring ventilation cooling. They are particularly suited for scenarios where there is a need to cool the entire space within a device or system. For our target customers, who may require efficient cooling solutions for electronics, machinery, or larger industrial spaces, axial fans offer a reliable and effective method to ensure uniform cooling across the entire internal area of their equipment. Their ability to handle large volumes of air at low pressure makes them an excellent choice for widespread cooling needs, particularly in applications where space-saving and efficiency are key concerns.
CCHV Popular DC Axial Fans
 |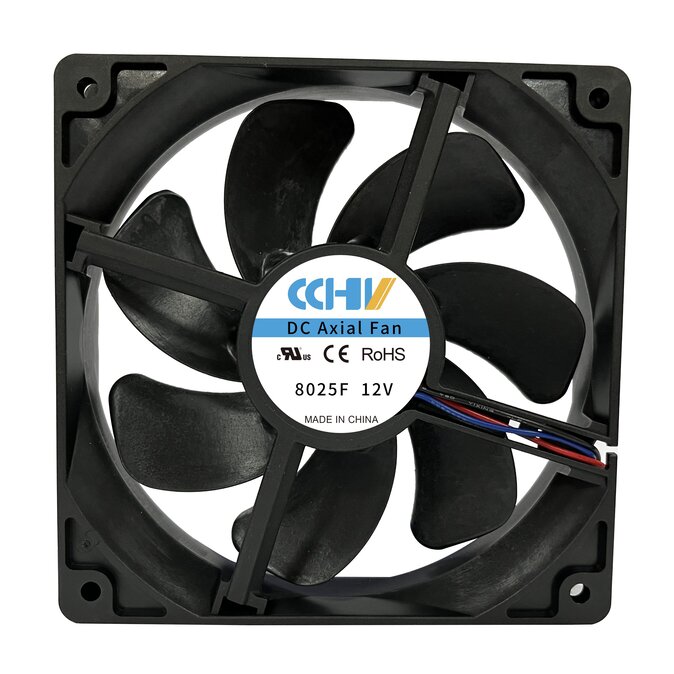  |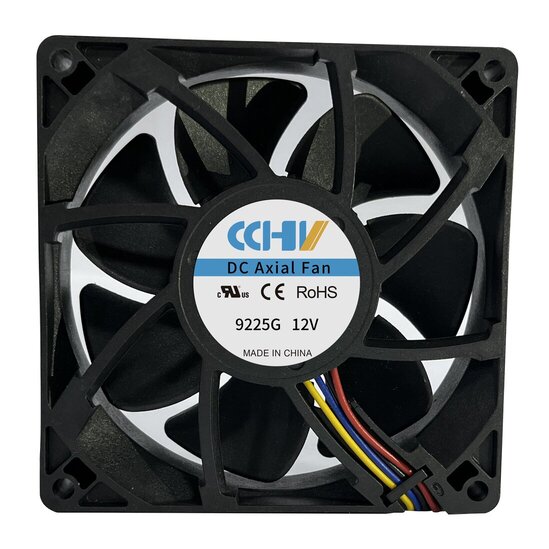  |  |
| 60X60X25MM Series C Click for Datasheet | 80X80X25MM Series F Click for Datasheet | 92X92X25MM Series G Click for Datasheet | 120X120X38MM Series D Click for Datasheet |
Delving into Centrifugal Fans
Centrifugal Fans Designes and Working Principle
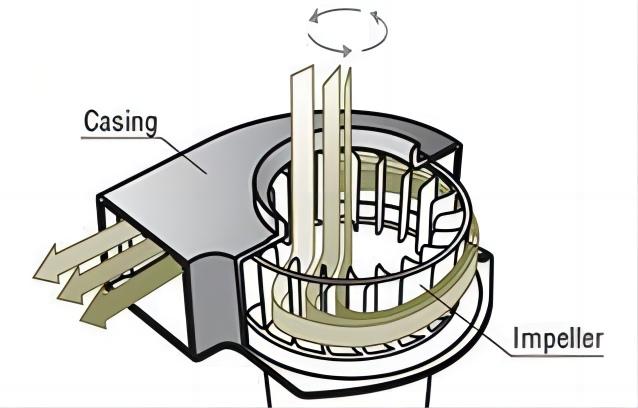
Centrifugal fans, sometimes also referred to as radial fans or DC centrifugal blowers. They operate on a mechanism that enhances air pressure by channeling airflow through a conduit. Its impeller is designed to generate a vortex, pulling air into the center of the fan and then expelling it perpendicularly. The centrifugal force produced by the cylindrical rotor with forward-curved blades creates a flow largely perpendicular to the axis of rotation. This rotation, in turn, arranges the airflow in a unidirectional pattern, effectively increasing the pressure.
 |  |
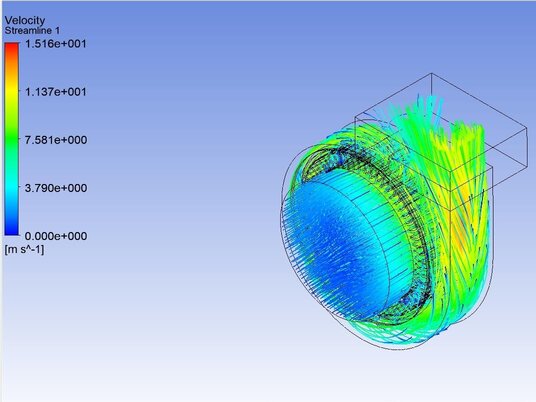 Impeller is designed to generate a vortex, pulling air into the center of the fan. | 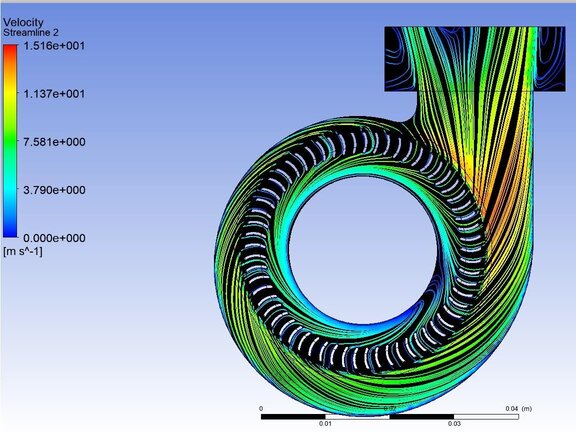 Air flow is expelled perpendicularly to the axis of rotation. |
The unique aspect of a centrifugal fan lies in its volute or scroll casing, which transforms part of the dynamic pressure into static pressure. This casing, shaped in a gradually widening Archimedean spiral, decreases the airspeed while simultaneously increasing static pressure. This design feature is critical in reducing the airflow and enhancing air pressure, making the centrifugal fan efficient for applications requiring directed, high-pressure airflow.
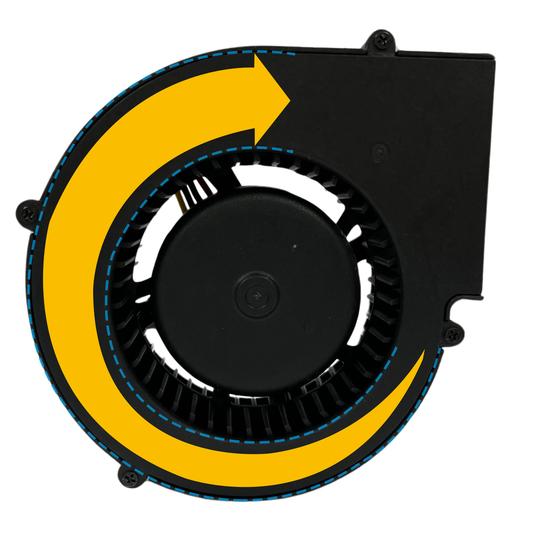

Typical applications
Centrifugal fans, designed with a narrowed exhaust for concentrating air in a specific direction, are primarily utilized for targeted cooling applications. Their high static pressure makes them especially suitable for situations where air movement is constrained or in scenarios where air needs to be distributed through ducts.
It is essential for precision cooling in electronics, automotive HVAC systems, and industrial machinery. They ensure effective temperature control in vehicles, including buses and refrigerated trucks, and maintain optimal conditions in residential and commercial spaces. These fans are also crucial in specialized equipment like medical devices, offering consistent, reliable cooling across various sectors.
CCHV Popular DC Centrifugal Fans
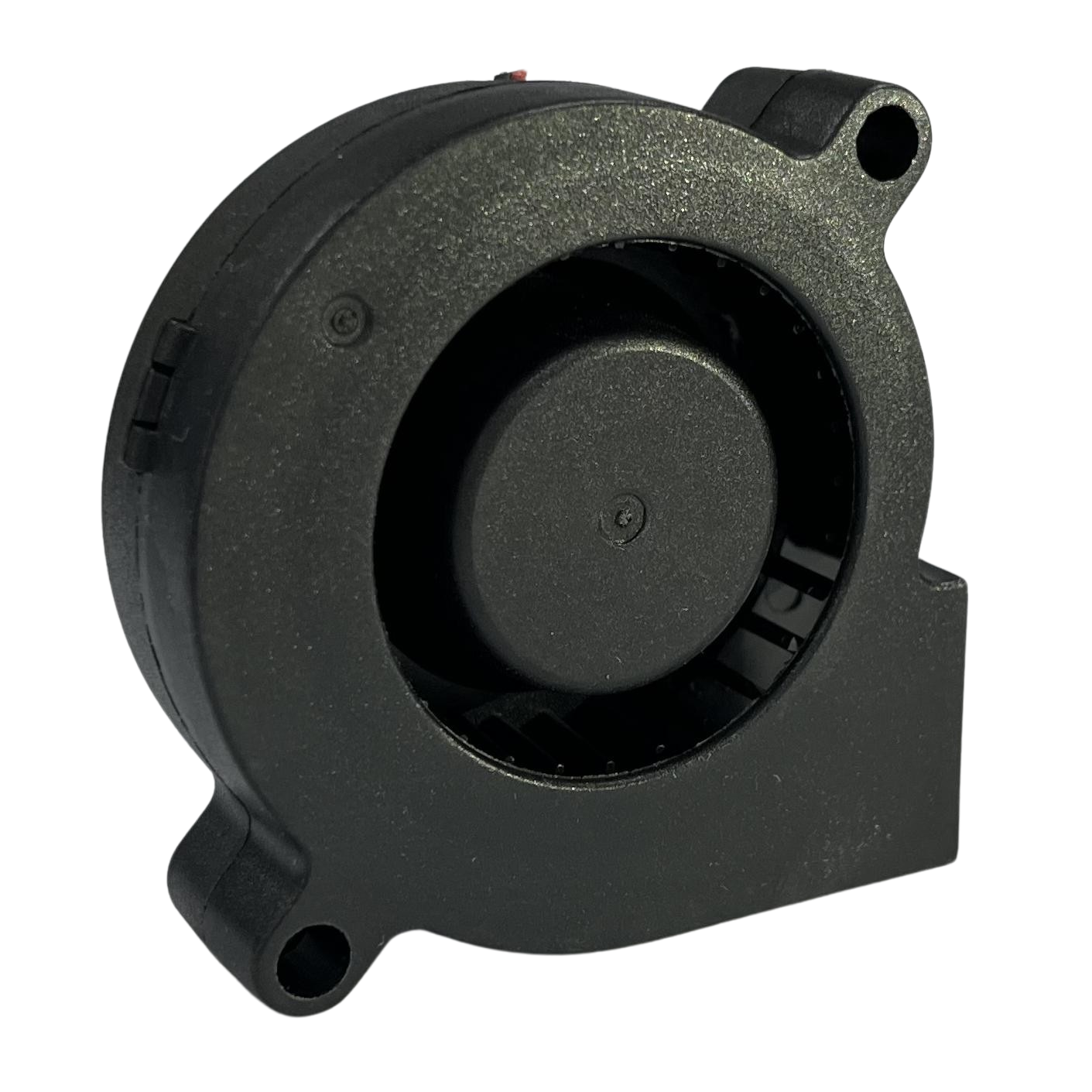 |  |  |  |
| 50X50X15MM Series C Click for Datasheet | 75X75X30MM Series D Click for Datasheet | 97X97X33MM Series B Click for Datasheet | 97X97X33MM Series B Click for Datasheet |
Comparing Axial Fans and Centrifugal Fans
To comprehensively compare axial and centrifugal fans, it’s crucial to analyze them on an equal footing – same size, voltage, and speed. Considering that, for instance, a DC axial fan measuring 60x60x25mm operating at 4500RPM versus a DC centrifugal fan of 60x25mm at the same 4500RPM. This case study approach allows for a vivid and fair analysis of the differences between these two types of fans. By matching their operational parameters, we can delve into an insightful exploration of how each fan type performs under similar conditions, examining aspects such as airflow direction, pressure generation, noise levels, and energy efficiency.
| Rated Voltage | Speed (RPM) | Operated Current (A) | Power (W) | Max. Air Flow (cfm) | Max. Air Pressure mmAQ | Noise (dBA) | |
| 60x60x25mm Axial | 12V | 4500 | 0.08 | 0.96 | 21.53 | 6.45 | 32.9 |
| 60x25mm Centrifugal | 12V | 4500 | 0.32 | 3.84 | 9.17 | 23.58 | 45.2 |
From the form as above, we can easily come to know that,
- Power Consumption and Current: The axial fan operates at a lower current of 0.08A, consuming 0.96W of power. In contrast, the centrifugal fan requires a higher current of 0.32A, with a power consumption of 3.84W.
- Air Flow and Air Pressure: The axial fan has a maximum air flow of 21.53 cfm (cubic feet per minute) and an air pressure of 6.45 mmAQ. The centrifugal fan, on the other hand, produces a lower air flow of 9.17 cfm but a significantly higher air pressure of 23.58 mmAQ.
- Noise Level: The axial fan has a noise level of 32.9 dBA, whereas the centrifugal fan is louder at 45.2 dBA.
From the analysis as above, the key differences between axial and centrifugal fans are evident:
| Axial Fans | Centrifugal Fans |
| Lower Current & Power Consumption | Higher Current & Power Comsuption |
| Higher Air Flow, but Lower Air Pressure | Lower Air Flow, but Higher Air Pressure |
| Lower Noise | Higher Noise |
| Airflow Parallel to The Axis | Airflow Perpendicularly to The Axis |
| For Entire Space Cooling Within A Device And System | For Targeted Cooling Applications |
| Lower Cost | Higher Cost |
Factors to Consider When Choosing Axials and Centrifugal Fans
When choosing between axial and centrifugal fans, several factors should be considered:
- Airflow Direction and Volume: Axial fans move a large volume of air in a straight line along the axis of the fan, ideal for non-ducted applications and larger spaces. Centrifugal fans, however, direct air at a right angle to the intake, making them suitable for ducted applications or where air needs to be directed more precisel.
- Pressure Requirements: Axial fans work well against low pressure, while centrifugal fans are more effective against higher pressure, making them suitable for applications requiring air to be moved through resistance like filters or duct.
- Noise Level: Centrifugal fans tend to be somewhat louder than axial fans, which should be considered in noise-sensitive environment.
- Energy Efficiency: While axial fans require less power for operation, centrifugal fans are generally more energy-efficient, especially in constant airflow application.
- Space and Size Constraints: Axial fans are typically more compact and can be a better choice in limited spaces. In contrast, centrifugal fans might require more space due to their different air direction and pressure capabilities.
These factors help in determining the most suitable fan type for specific applications, based on airflow requirements, space constraints, noise levels, and energy efficiency.
Conclusions
The comparison and insights provided on axial and centrifugal fans are crucial in guiding readers to make an informed choice when selecting a fan type. When choosing between axial and centrifugal fans, it’s important to consider specific application requirements and environmental factors. Axial fans, known for their ability to move air efficiently along their axis, are ideal for environments where high airflow is needed across large spaces. They are typically quieter and consume less power, making them suitable for general ventilation and cooling tasks. On the other hand, centrifugal fans, with their radial air movement, are designed for applications that require air to be moved at higher pressures. They excel in situations where air needs to be directed through ducts or for localized cooling. These fans are often more robust and can handle more challenging environmental conditions. In summary, the choice between an axial and a centrifugal fan hinges on the specific requirements of airflow direction, pressure, noise level, energy efficiency, and the physical environment where the fan will operate.
FAQs
Q1: What are the key differences between axial and centrifugal fans?
A1: Axial fans move air along their axis, offering higher airflow over large areas, whereas centrifugal fans direct air radially and are better for directed airflow or higher pressure applications.
Q2: How do noise levels compare between axial and centrifugal fans?
A2: Centrifugal fans tend to be louder than axial fans due to their operation method and airflow direction one same size and speed. However, advancements in design and technology have mitigated noise levels in many modern fan models.
Q3: Why does the centrifugal fan have a higher operating current than the axial fan?
A3: The centrifugal fan requires more power to generate higher pressure, which reflects in its higher operating current.
Q4: Why does the axial fan have a higher air flow than the centrifugal fan?
A4: Axial fans are designed to move air along the axis of the fan, meaning they work by pushing air in a direction that is parallel to the shaft where the blades rotate. This design allows for a larger volume of air to be moved across the fan blades in a straight line, which is efficient for moving air over long distances and results in a higher cubic feet per minute (CFM) rating, indicative of higher airflow.
Q5: Why does the centrifugal fan have a higher air pressure than the axial fan?
A5: The unique aspect of a centrifugal fan lies in its volute or scroll casing, which transforms part of the dynamic pressure into static pressure. This casing, shaped in a gradually widening Archimedean spiral, decreases the airspeed while simultaneously increasing static pressure.